Orthopedic & Rheumatologyal Care
Strengthening Joints, Restoring Mobility
Expert care for bones, joints, muscles, and autoimmune conditions like arthritis and osteoporosis. Our integrated orthopedic and rheumatology services focus on pain relief, improved mobility, and long-term joint health for a more active life.
Ankylosing spondylitis
Bones are among the strongest materials in the human body, with 206 bones connected by ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. They play key roles—providing structure, protecting organs, and storing essential minerals like calcium. Building strong bones during childhood is crucial, as bone mass peaks around age 30. As we age, bone remodeling occurs, and bone density gradually decreases. This natural loss makes older adults more vulnerable to bone-related diseases. Common conditions include osteoporosis, arthritis, osteomalacia, spondylitis, and osteopenia.
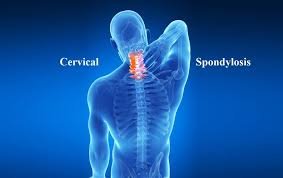
Cervical Spondylosiss
Cervical spondylosis, also known as cervical osteoarthritis or neck arthritis, is a common age-related condition affecting the joints and discs in the neck. It typically begins after the age of 30 due to the gradual wear and tear of bones and cartilage in the cervical spine. While many people may never experience symptoms, others may develop chronic stiffness, pain, and reduced mobility. Individuals with low bone density or inadequate calcium intake are at higher risk of developing this condition.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a chronic condition characterized by widespread pain and associated disability. It often coexists with medically unexplained symptoms and affects about 2–3% of people in the UK and US. FM can occur at any age but is most common in women over 70, with a strong female predominance (10:1). Risk factors include unresolved psychological stress, poor sleep, prior injuries, and low socioeconomic status. FM can also occur alongside other rheumatic conditions like axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and lupus (SLE).
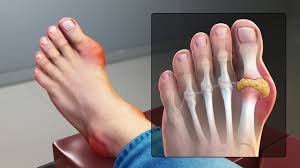
Gout
Gout is a metabolic disorder caused by the buildup of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of monosodium urate crystals in the joints. This condition results in severe pain, swelling, and inflammation, especially in the big toe joint, known as Podagra. Gout is more common in men after age 20 and in women after menopause. Uric acid levels above 7.0 mg/dL in men and 6.0 mg/dL in women increase the risk. Normally, uric acid is excreted by the kidneys, but overproduction or poor elimination causes crystal deposits. It has historically affected notable figures and is linked to lifestyle, diet, and genetics.
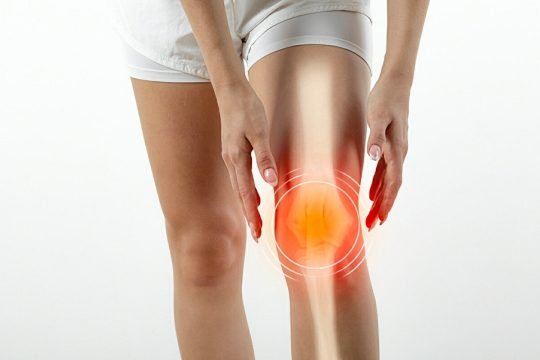
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis and a leading cause of pain and disability among older adults. It is marked by the gradual loss of articular cartilage, thickening of the underlying bone (subchondral sclerosis), formation of bone spurs (osteophytes) around joint edges, and changes in joint shape, often resulting in joint enlargement and reduced mobility.
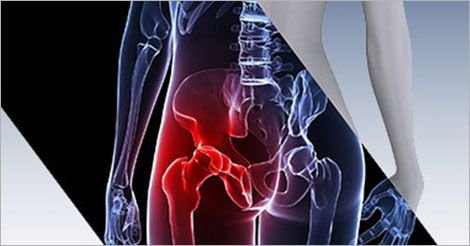
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is the most common bone disease, causing over 8.9 million fractures annually worldwide. About one-third of women and one-fifth of men over 50 will experience a fracture due to osteoporosis or osteopenia. The global burden is expected to rise 2–3 times by 2050 due to population aging. Diagnosis remains low, especially in rural Asia, due to limited access to DXA scanning. Common fracture sites include the spine, hip, forearm, and humerus, with hip fractures being the most severe. These carry a 12% immediate mortality rate and significantly increase long-term health risks and costs.
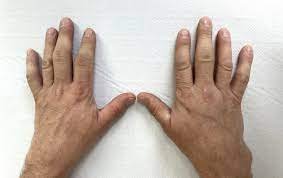
Rheumatoid
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory joint disorder that affects people of all ethnicities worldwide. Its prevalence ranges from 0.8% to 1% in Europe and South Asia, with a higher incidence in women (3:1 female-to-male ratio). The condition is less common in Southeast Asia (0.4%) but reaches up to 5% among the Pima Indians. RA typically follows a course of flare-ups and remissions, leading to progressive joint damage if left untreated.
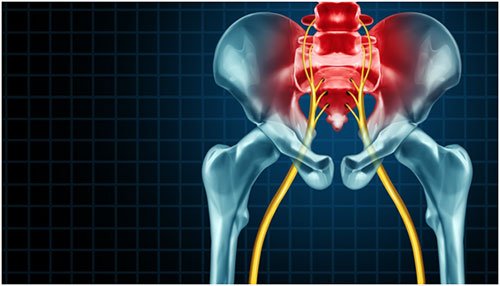
Sciatica
Sciatica is not a disease but a collection of symptoms including sharp or pricking pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness that begins in the lower back and radiates down through the buttocks, legs, and into the foot. The primary cause is the compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, often due to a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or injury.
Lumbar spondylosis
Sciatica is not a disease but a collection of symptoms including sharp or pricking pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness that begins in the lower back and radiates down through the buttocks, legs, and into the foot. The primary cause is the compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, often due to a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or injury.
