Eczema
Introduction
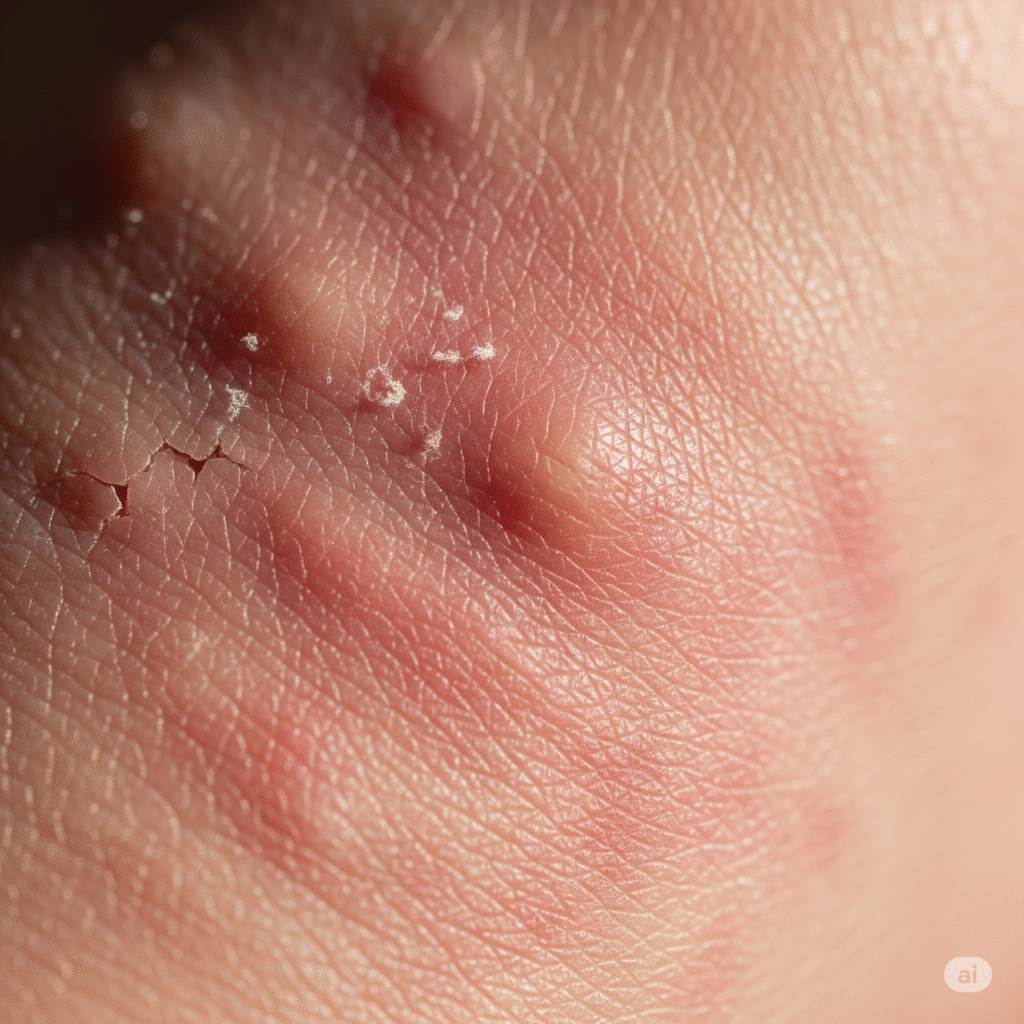
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition, characterized by redness, itching, dryness and skin irritation. This usually affects children but can occur at any age. Eczema is not contagious, but runs in families with a history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed that it involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors that weaken the skin obstruction, making it more susceptible to irritability and allergies.
Types of Eczema
Atopic dermatitis
A chronic, itching inflammation of the skin that often begins in childhood and is associated with asthma or grass fever.
Contact dermatitis
Directly exposure to skin causes contact with hurdles or allergies such as soap, detergent or some metals.
Neurodermatitis
Repeated scratches or rubbing were triggered, resulting in thick, crust patches on the skin.
Fusion binding
Poor blood circulation occurs in the lower legs, often with inflammation and varicose veins.
Causes Of Eczema
- Eczema, asthma, or allergic family history increases the risk.
- Genetic mutation weakens the protective barrier of the skin.
- A highly active immune system causes excessive inflammation..
- Exposure for allergies such as dust particles, pollen, or pet dander trigger triggers symptoms.
- Contact with irritability such as soap and detergent damages sensitive skin.
- Cold, dry or air weather can dry and flare the skin.
- Emotional stress deteriorates itching and inflammation.
- Food allergies such as milk, eggs, or peanuts can trigger eczema, especially in children.
- Bacterial, viral or fungal infections can spoil symptoms.
- Wool or synthetic ingredients such as wearing rough clothes disturb the skin.
- Frequent bathing or hot rain strips natural oils with skin.
- Excessive sweating and heat can trigger itching and redness.
Clinical features of Ecezma:
Itching
Constant itching causes discomfort, deteriorates at night, and leads to scratches.
Redness and swelling
The skin becomes red, swollen and swollen due to overrition of the immune system.
Dry and crushed skin
Loss of moisture causes dry, rough, flaky skin that is easily irritated.
Fafole or ozing wounds
Small Blissors May Form, Burst, Ooze Fluid, and Create Crusty Patches.
Thick
Thickening of continuous scratches, it becomes darker in leather and dark colors.
Symptoms associated with Ecezma
- Severe itching continues and deteriorating at night, causing constant scratches.
- Severe itching continues and deteriorating at night, causing constant scratches.
- Red and inflamed patches appear, which show symptoms of irritation and sensitivity.
- Cracks develop into the skin, especially on hands, feet or joints.
- A irritation or stinging sensation occurs on a cure or swollen skin areas.
- Flooding and scratch can develop malaise or dark patches.
- Fallas filled with small fluids may appear, which can create crusts and crusts.
- Due to repeated scratches, the skin becomes thick and becomes leather over time.
Investigations in Ecezma
- Diagnosis is mainly based on the physical examination of the skin and the history of the patient.
Doctors assess for personal or family history of eczema, asthma or allergies.
Identify specific allergies or irritability, causing allergic contact dermatitis.
A small skin sample can be taken to control other skin conditions.
Helps in detecting specific food or environmental allergies associated with provoking.
When the infection is used, the infection is suspected of identifying the motivational organism.
Elevated eosinophils or signs of inflammation in chronic cases can be revealed.
