Fungal Infection
Introduction
Fungal infection, also known as Mycos, is caused by fungi that invades the skin, nails, hair or internal organs. The fungi thrives in a warm, moist environment and can affect anyone, especially weaker immune systems or poor hygiene. These infections can range from mild and superficial to severe and systemic. Most fungal infections are not life-threatening, but can cause significant discomfort, itching, and skin damage when untreated.
Types of Fungal Infection
Tinea corpooris
An infectious infection that appears in the form of red, circular, crust patch on the body.
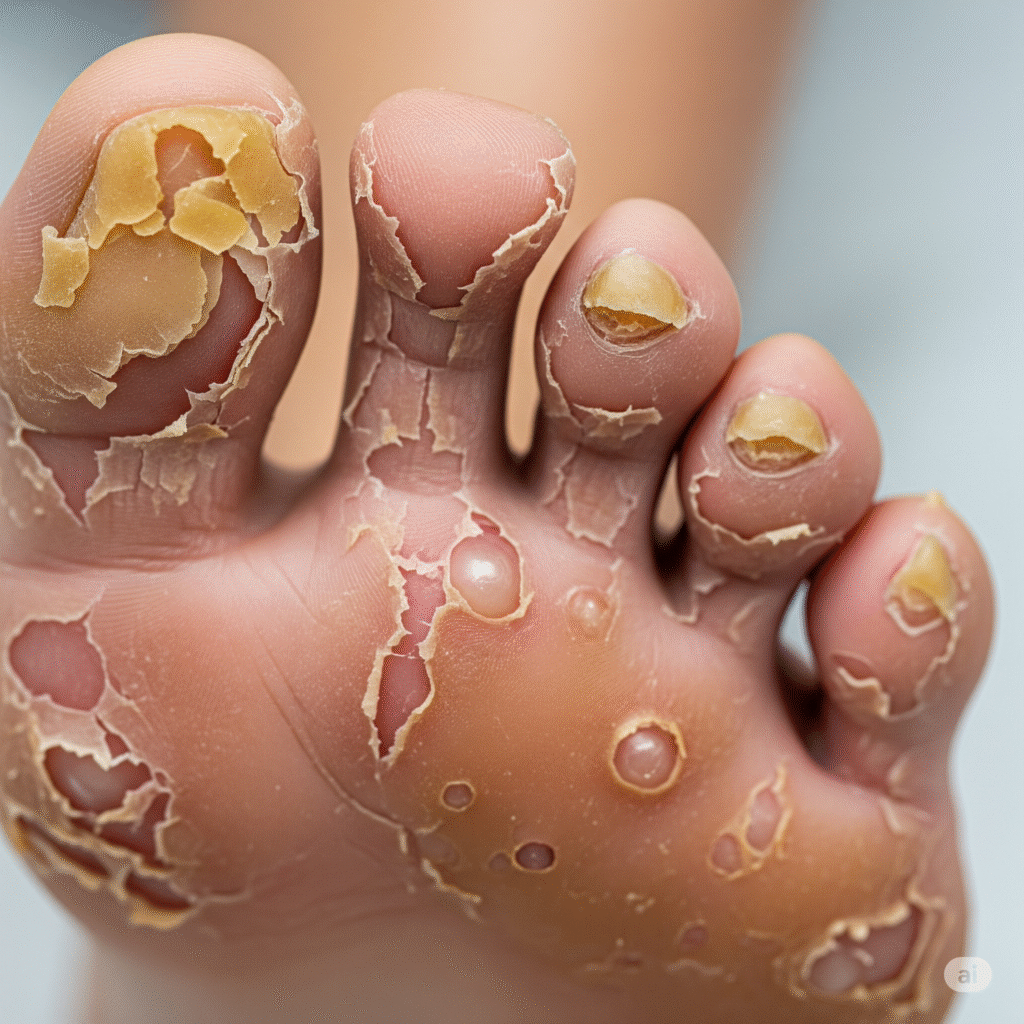
Tinia Pedis
Affects the legs, especially between the toes, itching, peeling and smell.
Tinea Unguium
A fungal infection of nails, which causes malaise, thickening and brittleness.
Tinia Versicoller
A superficial infection caused by the Malasaesia species, resulting in the patch on the skin is closed.
Causes of Fungal Infection
- Hot and humid weather creates an ideal environment for fungus growth on the skin.
- Poor hygiene practices allow the fungus to easily flourish and spread in the body.
- Weak immune system enables the body to fight fungus infections.
- Excessive sweating keeps the skin moist, especially in folds, encourages fungus buildups.
- Sharing individual items such as towels, shoes or razers can transmit fungal organisms.
- synthetic fabric mesh increases the risk of heat and moisture, infection.
- People with diabetes are more prone to fungus infections due to high sugar.
- Long -term use of antibiotics or steroids can irritate natural skin flora.
- Walking barefoot in public places increases contact with fungi on surfaces.
- Obesity leads to more skin folds where fungi can grow easily.
- Skin cuts or injuries provide entry points for fungal organisms.
Clinical features of Function Infection:
Redness and itching
Infected areas become red, swollen, and cause acute itching or irritation.
Scaling and peeling skin
The skin can be dry, flaky, or peel, especially around infected areas.
ring -shaped rash
Many fungal infections, such as ringworms, appear as round patches with raised edges.
Flaws in Skin
Skin, especially between the toes or in the folds, may be crack or divided by pain.
skin malaise
Fungus infections can cause yellow, white or brown malaise of nails or patch on the skin.
Symptoms associated with Fungal Infection
- Itching and redness appear on the affected areas of the skin.
- The skin becomes crushed, dry, and slowly starts peeling.
- Circular rashes with raised edges can develop on the skin.
- The form of cracks or division, especially between toes or fingers.
- The nails become thick, brittle, and gradually turn into color.
- Burning is felt in infected or irritated skin areas.
- White patches can be made inside the mouth or tongue.
- Dishonesty can smell from infected legs or nails.
Investigations in Fungal Infection
- Doctors observe the affected skin, nails or mucous membranes for specific fungus signals.
A skin, hair, or nail scraping is examined under a microscope with koh to detect fungi elements.
Samples are placed in a culture medium to develop and identify specific types of fungi.
In vague or severe cases, a small skin sample is taken for histopathological examination.
A special UV light is used to check the skin; Some fungal infections flower under this light.
Systematic fungus infections to examine the immune response or detect fungal antigens.
A molecular test is used to detect fungi DNA, which is helpful in systemic or resistant infections.
