Gastrointestinal & Hepatobiliary
Digestive Health (Gastrointestinal Disorders)
The gastrointestinal system includes the stomach and intestines and is essential for proper digestion. Common disorders like gastritis, indigestion, ulcers, and bloating can cause discomfort and impact overall health. A balanced diet, hydration, and timely treatment are key to maintaining digestive wellness.
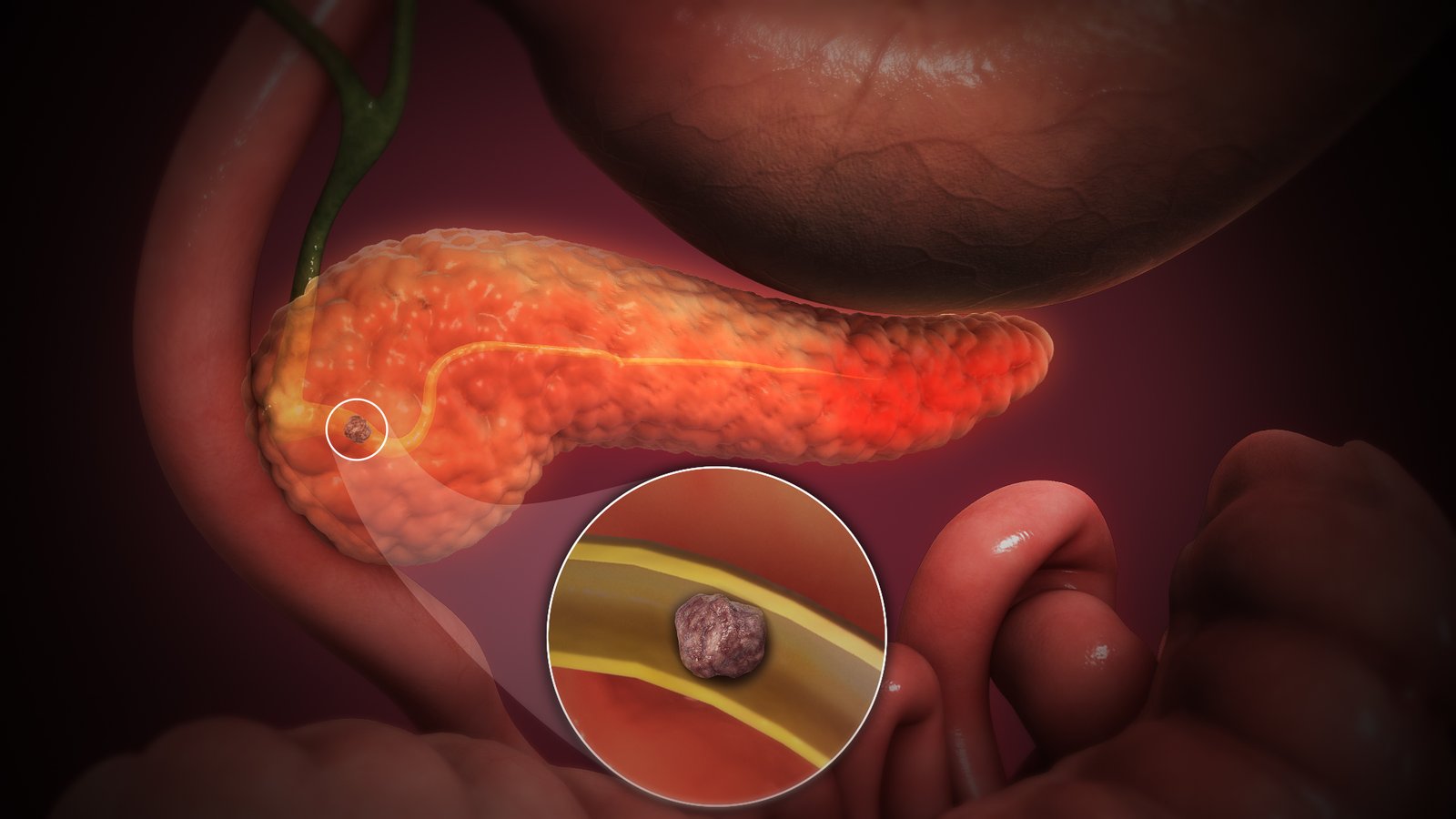
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas, a gland that helps with digestion and blood sugar control. It usually occurs due to gallstones, heavy alcohol use, or certain medications. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. Inflammation can range from mild to life-threatening in severe cases. Prompt medical treatment is essential to manage pain and prevent complications.
Constipations
The human body runs on a biological clock that controls key functions like digestion, sleep, and excretion. Excretion is vital for removing waste and supporting overall health. When bowel movements become infrequent or difficult, it leads to constipation—a common issue caused by poor intestinal function. Constipation happens when the large intestine can't move stool properly, making defecation hard or painful. If ignored, it can lead to other health problems. Ayurveda offers natural relief through herbs like Amalaki, Haritaki, Bibhitaki, Punarnava, and Kalmegh, available in formulations like Triphala capsules and Kumaari Saar by Planet Ayurveda.
Chronic pancreatits
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term inflammation of the pancreas that leads to permanent damage. It is often caused by prolonged alcohol use, genetic factors, or repeated episodes of acute pancreatitis. Common symptoms include persistent abdominal pain, weight loss, and digestive issues. Over time, the pancreas may lose its ability to produce enzymes and insulin. Treatment focuses on pain management, enzyme replacement, and lifestyle changes to prevent further damage.

Diarrhoea
Diarrhea is a very common health issue that can range from mild to severe. It is marked by frequent, loose, and watery stools, often accompanied by discomfort and cramping. The condition is usually caused by infections in the gastrointestinal tract or by consuming contaminated food or water. Prompt care is important to prevent dehydration and complications.
Gastritis
Gastritis is a condition where the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or irritated. It can be caused by infection (like H. pylori), excessive alcohol use, spicy food, stress, or certain medications. Common symptoms include stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and loss of appetite. It may be acute or chronic, depending on the cause and duration. Treatment includes avoiding triggers, dietary changes, and medications to reduce stomach acid.
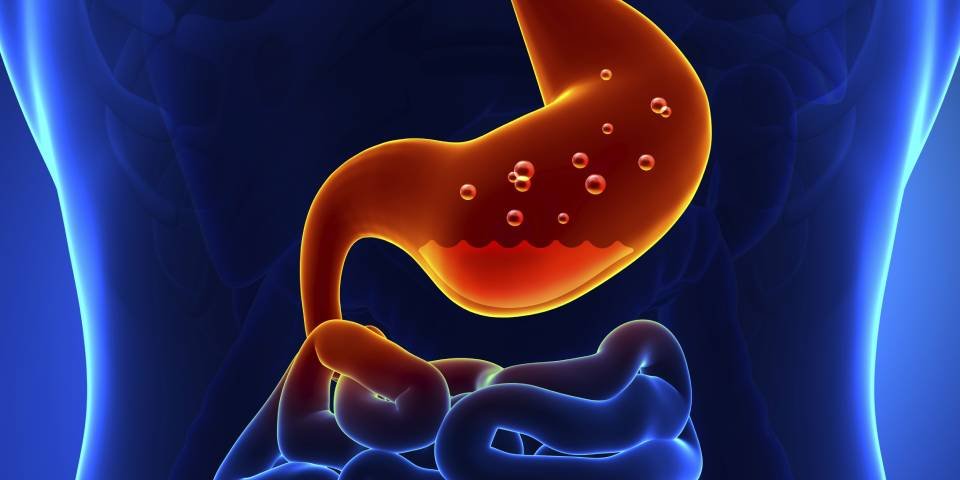
Gastro-oesophageal reflux
Gastro-oesophageal reflux is a condition where stomach acid flows back into the food pipe (esophagus). This backflow causes irritation, leading to symptoms like heartburn, chest pain, sour taste, and difficulty swallowing. It often occurs after meals or when lying down. Common causes include overeating, obesity, smoking, or a weak lower esophageal sphincter. Treatment involves lifestyle changes, avoiding trigger foods, and medications to reduce acid production.
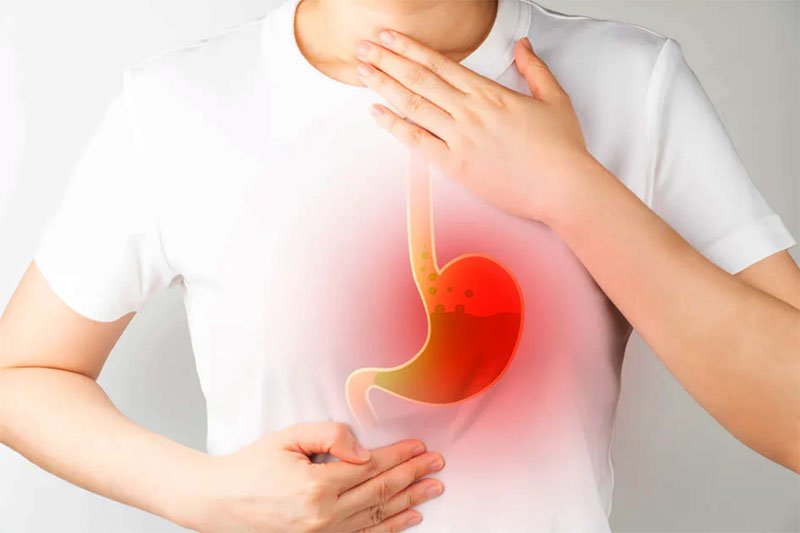
Hyperacidity
Hyperacidity is a condition where the stomach produces excessive acid, leading to discomfort and digestive issues. It often results in symptoms like heartburn, stomach pain, acid reflux, bloating, and nausea. Common causes include unhealthy eating habits, stress, spicy foods, and irregular meal timings. If left untreated, it can lead to ulcers or inflammation of the stomach lining. Treatment includes dietary changes, stress management, and antacid medications to control acid levels. Ask ChatGPT
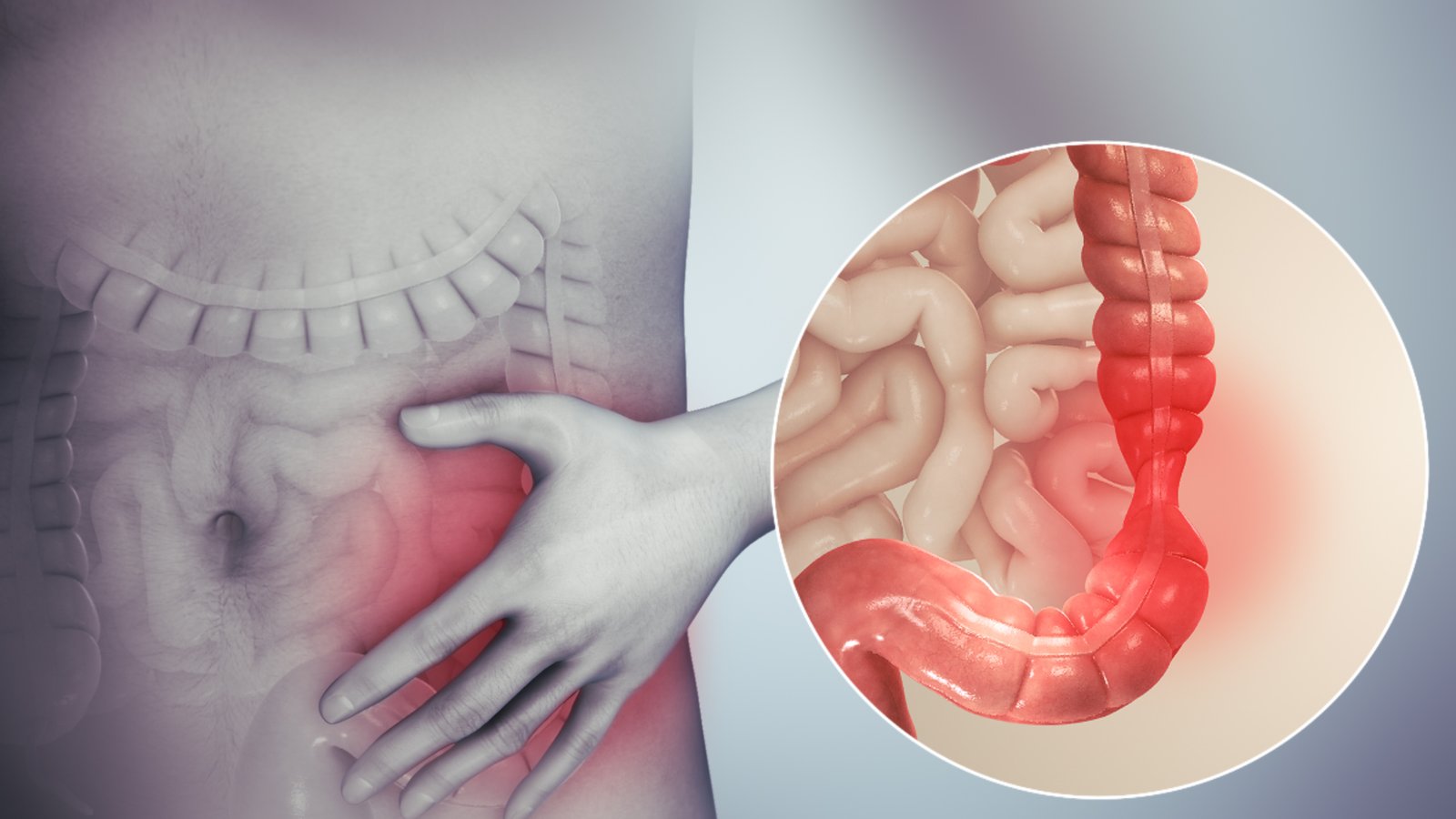
IBS (Irritable bowel syndrome)
Indigestion is a common digestive disorder seen worldwide. In today’s fast-paced lifestyle, many people neglect proper diet, exercise, and daily routines. Healthy meals are often replaced with junk food and processed snacks, leading to poor digestion. This shift contributes to various gastric issues like dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), as weak digestion is often the root cause of many health problems. Maintaining a balanced diet and healthy habits is essential for good digestive health.

Inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) refers to chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, mainly including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. It causes symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue. The exact cause is unclear but may involve the immune system and genetics. IBD has flare-ups and remission periods. Treatment includes medications, dietary changes, and sometimes surgery.
Malabsorption
Malabsorption is a condition where the body is unable to absorb nutrients properly from the food in the small intestine. It can lead to deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, proteins, and fats. Common symptoms include weight loss, diarrhea, bloating, and fatigue. Causes include celiac disease, lactose intolerance, pancreatic disorders, and infections. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve dietary changes, supplements, and medications. Ask ChatGPT
Peptic ulcer disease
Peptic ulcer disease occurs when open sores or ulcers develop on the inner lining of the stomach or upper part of the small intestine. It is commonly caused by infection with H. pylori bacteria or long-term use of NSAIDs like aspirin. Symptoms include burning stomach pain, nausea, bloating, and in severe cases, vomiting blood. Smoking, stress, and spicy foods may worsen the condition. Treatment includes antibiotics, acid-reducing medications, and lifestyle changes.
Liver Health (Hepatobiliary Disorders)
The hepatobiliary system, which includes the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts, supports digestion and toxin removal. Conditions such as fatty liver, hepatitis, and gallstones are common and may need medical attention. Healthy lifestyle habits and regular check-ups are crucial for liver care.
Alcoholic liver disease
Alcohol is a leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide, with rising consumption in many regions. Most heavy drinkers develop fatty liver, but only some progress to serious conditions like alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis. The risk of severe alcohol-related liver disease (ALD) depends on various factors, including drinking patterns, genetics, and overall health.
Autoimmune liver and biliary disease
The liver is a key organ affected by autoimmune diseases. The type of autoimmune response and the specific target cells determine the clinical features. When immune injury targets liver cells, it leads to autoimmune hepatitis, while damage to bile duct cells results in conditions like primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)—each with distinct disease patterns.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease marked by liver scarring (fibrosis) and nodule formation. It can occur at any age and is a major cause of portal hypertension and early death. Common causes include chronic hepatitis, excessive alcohol use, and NAFLD. It can also result from long-term bile duct damage (PBC, PSC) or impaired blood flow from the liver, as seen in Budd–Chiari syndrome and sinusoidal obstruction syndrome.
Gallstones
Gallstones are a common digestive issue, often causing upper abdominal or back pain lasting several hours, along with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, bloating, indigestion, and heartburn. North India, especially cities like Chandigarh and New Delhi, reports a higher incidence of gallstones, affecting about 7.4% of the adult population. While once common in overweight women around age 40, gallstones are now increasingly seen in younger, slimmer women in their 20s. Women are more affected than men, with the highest risk seen in females aged 45–60.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) is fat buildup in the liver not caused by alcohol. It’s linked to obesity, diabetes, and poor lifestyle. It can progress from simple fat (steatosis) to inflammation (NASH), fibrosis, and even cirrhosis or liver cancer. NAFLD affects 24% of people worldwide and is a rising cause of liver transplants.
